Taxonomi - What does this service do?
This API is for organising and categorising the content provided by NDLA. At the heart of the structure are theresources, which represent the actual content, such as articles, videos of lectures, quizzes, learning paths (which are compositions of other resources) or any number of other media. The organisation of content allows for a context rich user interface to be built on top of this API where the content is displayed in context of asubject_and its_topics, with hyperlinks to related content.
Please note that this API is all about metadata. The actual content is stored in other APIs, identified by the content URI stored with each subject, topic and resource in this API.
The resources are categorised according to subjects and topics. A subject is a high-level field of study, such as Mathematics or Science, loosely based on the subject curricula atudir.no, whereas a topic is a hierarchical sub-division of the subject into subject areas. The topics may be loosely based on the subject areas atudir.no, or they may follow a different structure imposed by the editors.
This organisation gives us a tree representation of the content, where the subjects are at the roots of the tree, the topics make up the branches, and the resources are the leaves. Note, however, that this is not a strict tree-structure, since topics and resources may belong to several parents (see "Multiple parent connections" below).
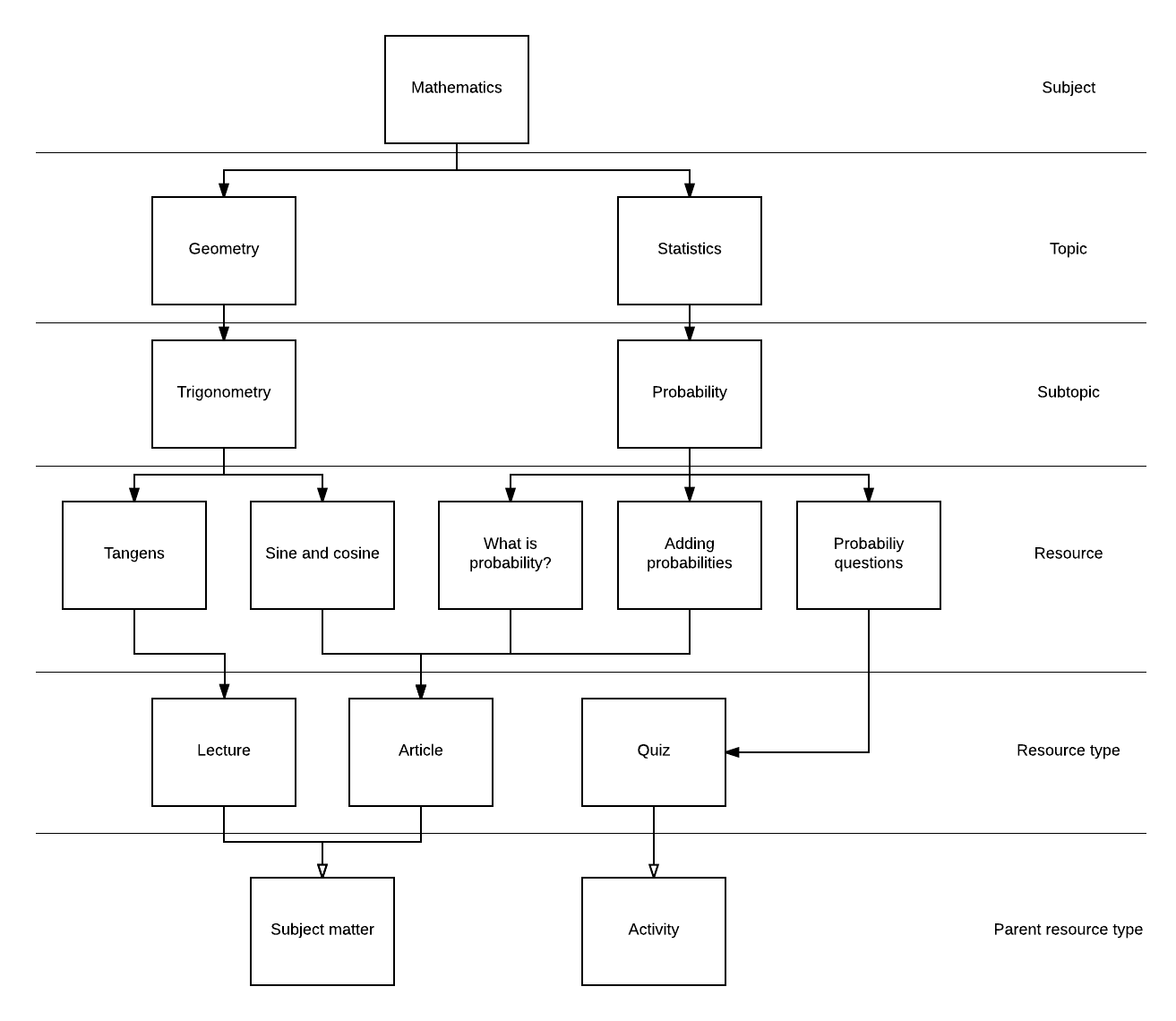
The taxonomy data model consists of_entities_and_connections_between entities.
The entities in the taxonomy are Subject, Topic, Resource, and Resource type. The taxonomy stores metadata for each entity, such as name and content URI. Translations of names can also be stored.
In addition to the entities, the taxonomy stores the connections you make between entities. Each connection also has metadata attached to it, such as which entities are connected, and whether or not this connection is the primary connection (see "Multiple parent connections" below). Subjects can be connected to topics, topics to subtopics, topics to resources, resources to resource types, and resource types to parent resources types.
Below you can see a figure of how entities can be connected. We will go through how this structure can be realised through the API. For details on the use of each service, please see the API documentation.